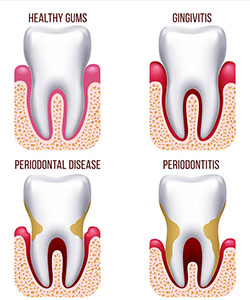
What is Periodontal (Gum Disease)?
Understanding Periodontal (Gum) Disease Periodontal disease, commonly known as gum disease or periodontitis, is an inflammatory condition that affects the soft tissues surrounding your teeth. In advanced stages, it can also damage the jawbone.
It often starts as gingivitis, a bacterial infection of the gums caused by plaque buildup. If left untreated, this infection can spread deeper into the gum pockets between your teeth, making it harder to remove. Over time, periodontal disease can destroy the connective tissues and bone, potentially leading to:
- Shifting or loose teeth
- Tooth loss
- Jawbone damage
Periodontal disease is the leading cause of tooth loss among adults worldwide. Early diagnosis, regular dental checkups, and proper oral hygiene are essential to preventing and managing this condition.
Types of Periodontal Disease
Without treatment, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of periodontal disease. As plaque toxins irritate the gums, the body’s inflammatory response causes the breakdown of bone and tissue. Common types of periodontal disease include:
- Chronic Periodontitis: The most common form, characterized by gum inflammation, deep pockets between the teeth and gums, and gum recession.
- Aggressive Periodontitis: Occurs in otherwise healthy individuals, often progressing rapidly with significant gum and bone destruction. It may run in families.
- Necrotizing Periodontitis: A severe condition marked by tissue death, most often seen in individuals with compromised immune systems or malnutrition
- Periodontitis From Systemic Disease: Associated with systemic health conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and respiratory disease.
Treating Periodontal Disease
Treatment for periodontal disease depends on the severity of the condition and the health of your teeth, gums, and jawbone. If detected early during the gingivitis stage, regular cleanings may be sufficient to restore gum health. However, in more advanced cases, specialized treatments may be needed:
Some common treatments for periodontal disease include
-
Scaling and Root Planning (Deep Cleaning): A non-surgical procedure where plaque and tartar are removed from above and below the gum line, and the roots are smoothed to promote healing. This is often done in sections under local anesthesia. Medications- Antibiotics, medicated mouth rinses, and electric toothbrushes may be recommended to help control infection.
-
Surgical Treatments: If deep pockets remain after scaling and root planning, periodontal surgery may be needed to reduce pocket depth and make it easier to clean the teeth.
-
In more severe cases, you may be referred to a periodontist, a specialist in gum and bone health
Common Periodontal Treatments
- Scaling and Root Planning: Deep cleaning to remove bacteria, plaque, and tartar from gum pockets. Prescription mouthwash and antibiotics may be used to control infection.
- Tissue Regeneration: Grafting procedures encourage the regrowth of lost bone and gum tissue
- Pocket Elimination Surgery (Flap Surgery): Reduces the size of gum pockets to facilitate cleaning and eliminate bacterial growth.
- Dental Implants: If teeth are lost due to gum disease, implants can restore function and aesthetics. In some cases, tissue regeneration may be necessary before implant placement.
Contact U9 Dental if you have any concerns about periodontal disease or treatment options
Maintenance
Maintaining Healthy Gums After Treatment Plaque can harden into tartar within 24 hours if not properly removed. While brushing and flossing help manage plaque buildup, professional cleanings are still essential, especially in areas that are hard to reach. After periodontal treatment, we recommend regular periodontal maintenance cleanings, typically four times a year. During these visits, we’ll monitor your gum pockets, remove plaque and tartar, and ensure your gums remain healthy. Your maintenance appointment will usually include:
- X-rays: To detect decay, bone loss, and other issues.
- Restoration Check: Evaluation of fillings, crowns, and other dental work.
- Cavity Inspection: A thorough examination for any signs of tooth decay
- Oral Cancer Screening: Examination of the face, neck, lips, tongue, and gums for oral cancer
- Oral Hygiene Guidance: Personalized recommendations for tools like electric toothbrushes, fluoride rinses, and special periodontal brushes.
- Teeth Polishing: Removal of surface stains and remaining plaque. Consistent oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings are key to keeping periodontal disease in check.
Contact our friendly staff at U9 Dental to schedule your appointment.